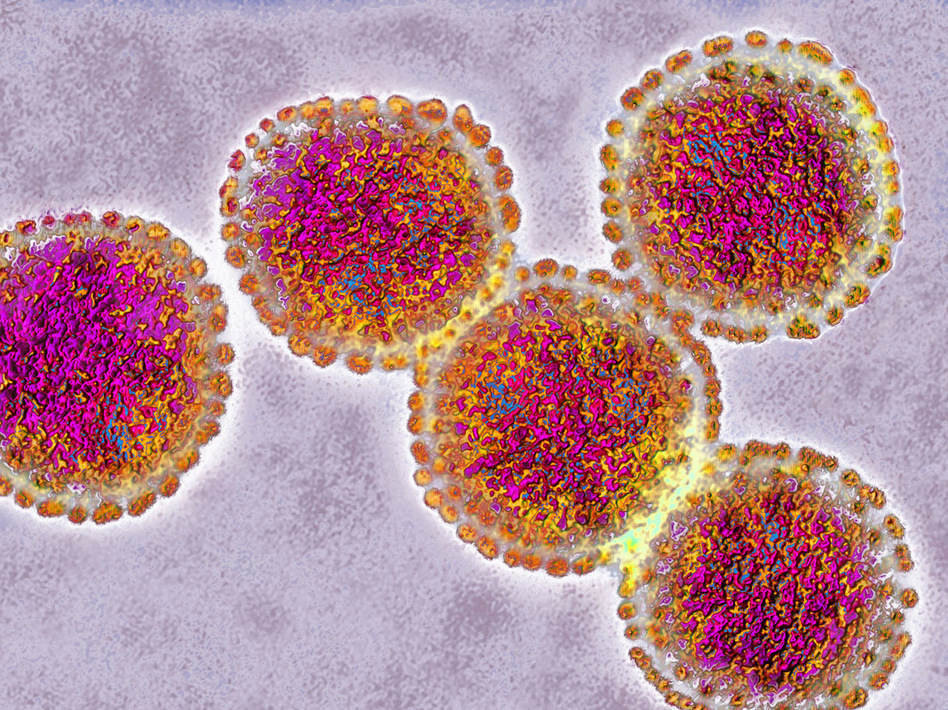
Bird flu virus milk has emerged as a potential concern, prompting investigations into the possibility of transmission through milk. This article delves into the evidence and explores the current understanding of this topic.
Understanding the transmission, symptoms, and prevention of the bird flu virus is crucial, and this article provides comprehensive insights into these aspects.
Bird Flu Virus Transmission

The bird flu virus, also known as avian influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory virus that can infect both birds and humans. The virus is primarily transmitted through contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids, including saliva, nasal secretions, and feces.
The virus can spread in several ways, including:
- Direct contact:Contact with an infected bird or its bodily fluids can transmit the virus to humans. This can occur through handling infected birds, cleaning their cages, or being in close proximity to them.
- Indirect contact:The virus can also be transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, such as clothing, equipment, or surfaces that have been in contact with infected birds.
- Aerosol transmission:The virus can become airborne through coughing, sneezing, or other respiratory secretions from infected birds. This can lead to the transmission of the virus to humans who inhale these aerosols.
In the past, the bird flu virus has spread through various mechanisms, including:
- Outbreaks in poultry farms:Large outbreaks of the bird flu virus in poultry farms have resulted in significant transmission to humans who work with or handle infected birds.
- Contact with wild birds:Humans who come into contact with infected wild birds, such as hunters or bird watchers, have also been infected with the virus.
- Travel to affected areas:Individuals who travel to areas where the bird flu virus is prevalent may be exposed to the virus through contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
Bird Flu Virus Symptoms: Bird Flu Virus Milk

The symptoms of the bird flu virus in humans can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Mild cases may only cause mild respiratory symptoms, while severe cases can lead to life-threatening complications.
Common symptoms of mild bird flu virus infection include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny nose
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Fatigue
Severe cases of bird flu virus infection can lead to more serious complications, including:
- Pneumonia
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Multi-organ failure
- Death
| Symptom | Mild Infection | Severe Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | Yes | Yes |
| Cough | Yes | Yes |
| Sore throat | Yes | Yes |
| Runny nose | Yes | Yes |
| Muscle aches | Yes | Yes |
| Headache | Yes | Yes |
| Fatigue | Yes | Yes |
| Pneumonia | No | Yes |
| ARDS | No | Yes |
| Multi-organ failure | No | Yes |
| Death | No | Yes |
Closing Notes

While the risk of bird flu virus transmission through milk remains uncertain, ongoing research and monitoring are essential to ensure public health and safety.